Table of Contents
Install Kubernetes in the Ubuntu Server
Prerequisites
- VirtualBox
- Ubuntu Server (3 VMs, 2 vCPU & 2 GB RAM each)
Links needs to handy
- Kubeadm Installation
- Creating cluster using kubeadm
- Docker install
- Weave CNI (If you would like to use Weave)
- Calico CNI (If you would like to use Calico)
- Kube-router CNI (If you would like to use Kube-router)
- Romana CNI (If you would like to use Romana)
- Flannel CNI (If you would like to use Flannel)
- OpenVSwitch CNI (If you would like to use OpenvSwitch)
How to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
I have already created a post for this. please check here
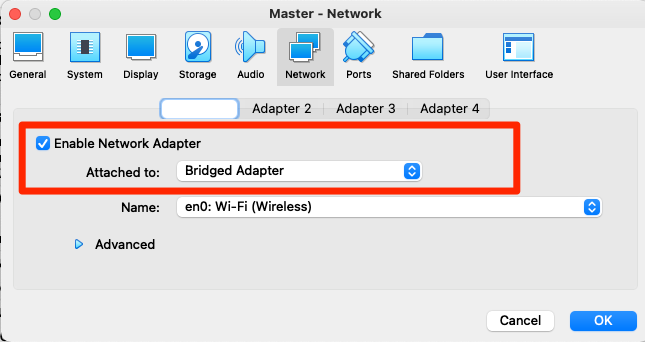
For this demo, I have deployed 3 Ubuntu server VM’s named it as Master, Node-1 & Node-2 and network is in Bridged Mode 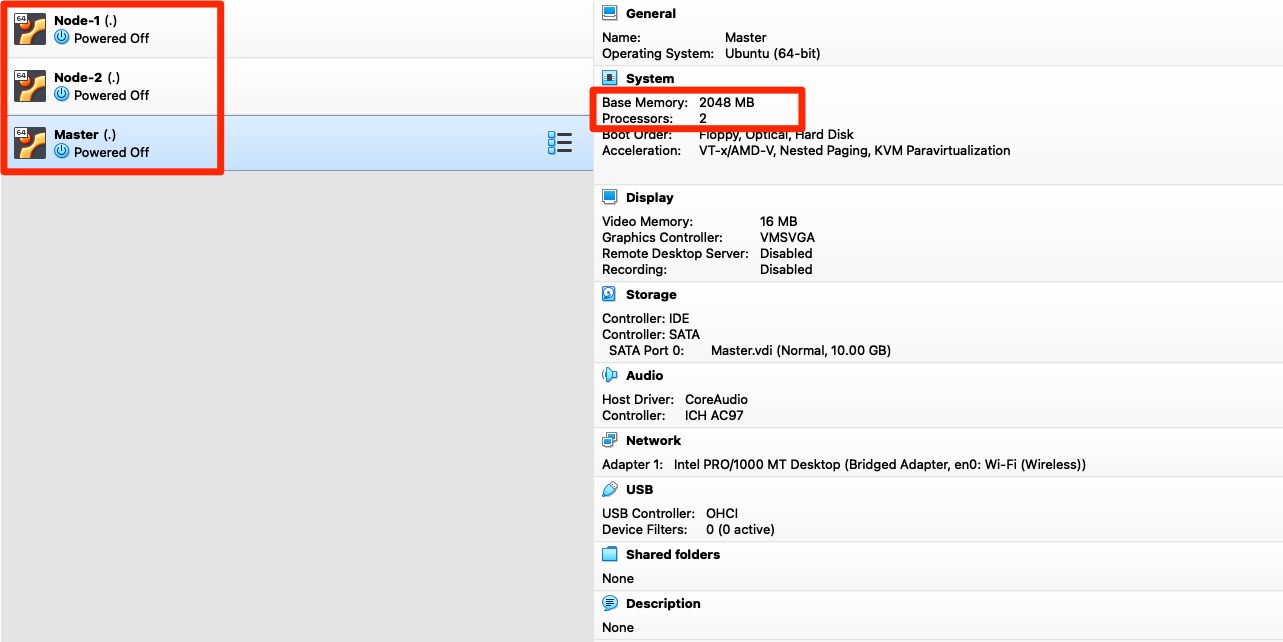
Customizations before installing k8
- Set Static IP to Linux machines [Link]
- Create DNS entries for name resolution
- Disable Swap on Linux machines [Link]
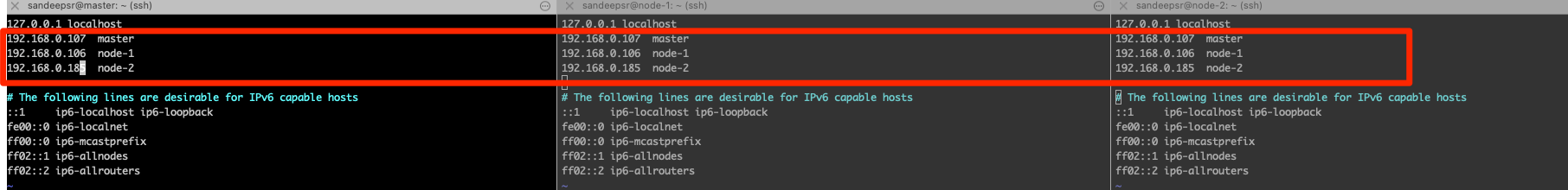
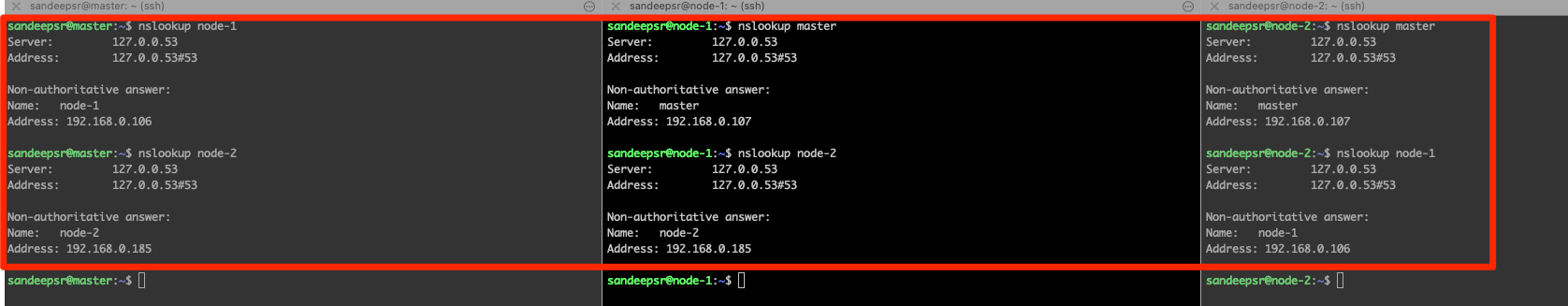
Please create static DNS records by adding entries to /etc/hosts file as shown below
Install Docker
For this lab setup we will use Docker as container runtime
Let’s install docker on all the VM’s – master , node-1 & node-2 by following this article
I have used below commands sequentially by following the article provided in above link
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg echo \ "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Install Kubernetes using Kubeadm
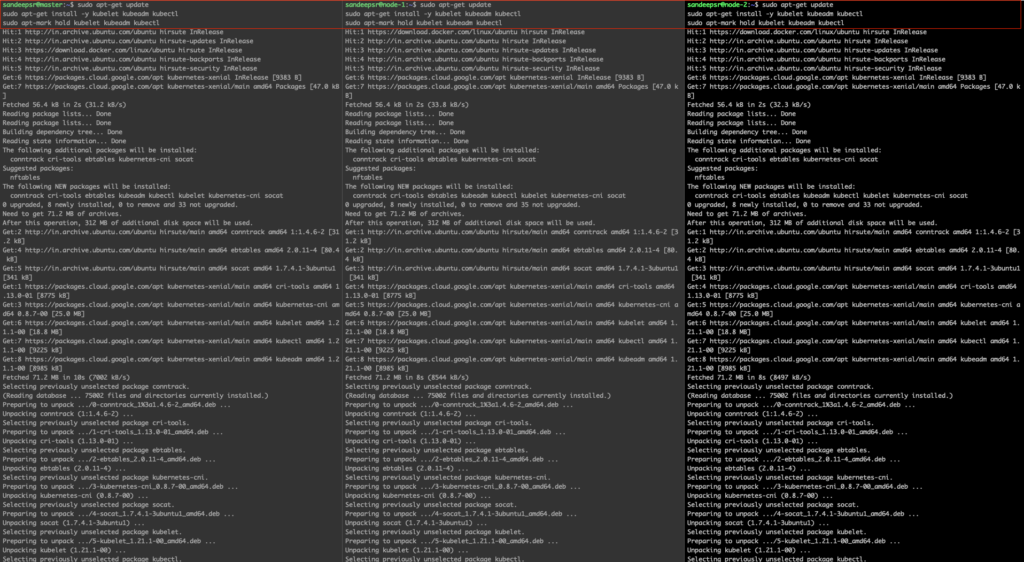
This installation is based on Kubernetes.io article and I ran the below commands sequentially on all Linux machines – master, node-1 & node-2
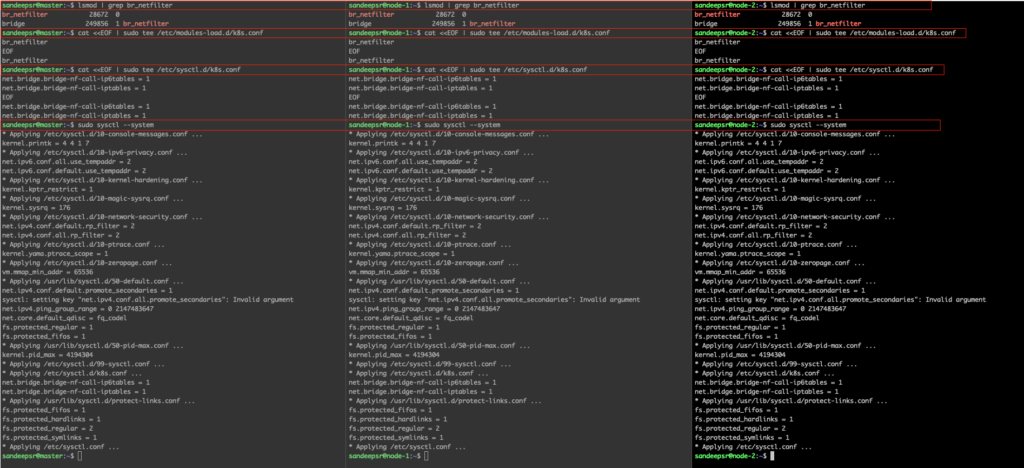
lsmod | grep br_netfilter sudo modprobe br_netfilter lsmod | grep br_netfilter cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf br_netfilter EOF cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 EOF sudo sysctl --system
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl sudo curl -fsSLo /usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Using kubeadm create Kubernetes cluster
This configuration is based on Kubernetes.io – creating a cluster with kubeadm and I ran the below commands sequentially on master vm only
Prerequisites
- static IP to master node – already set
- swap to be disabled – already set
- VM configuration 2 CPU & 2 GB RAM – already set
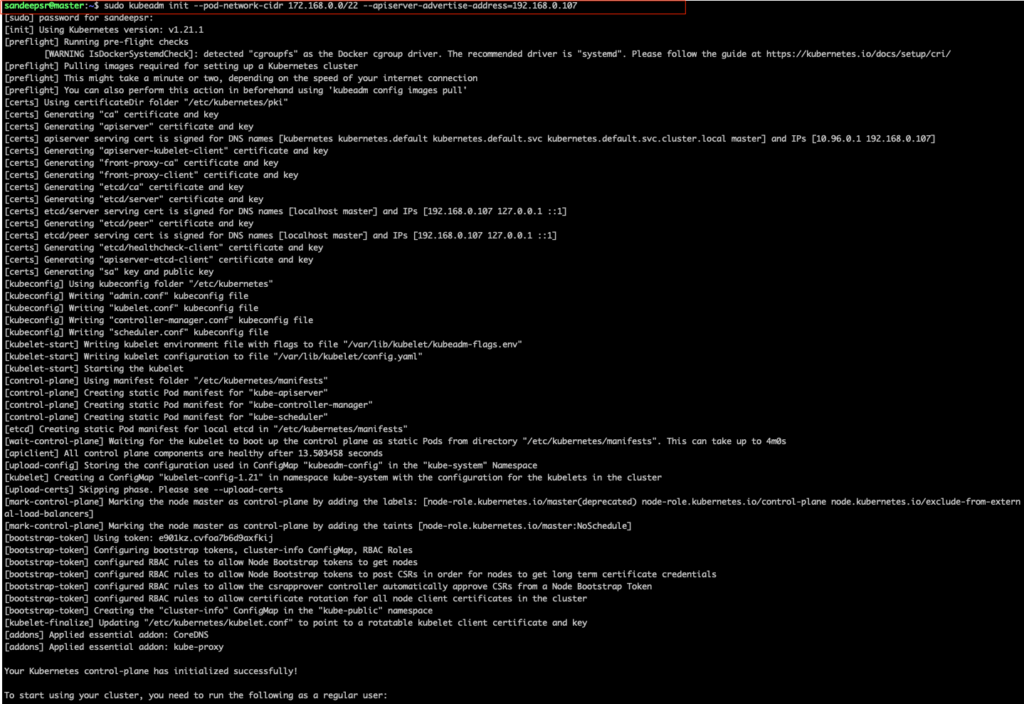
My master vm ip – 192.168.0.107
POD network subnet – 172.168.0.0/22 (you can choose what ever the subnet)
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr 172.168.0.0/22 --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.0.107
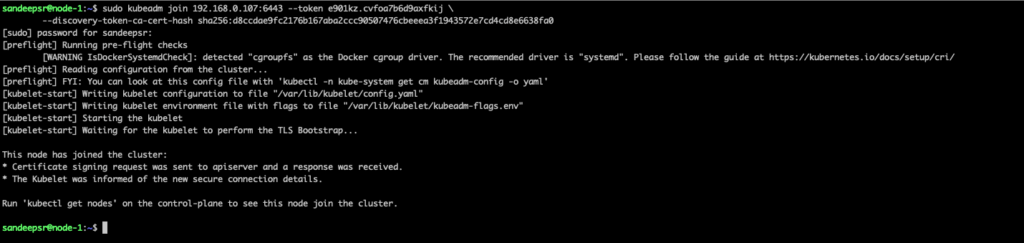
Please note the kubeadm join command and this will used to add the worker nodes to cluster
kubeadm join 192.168.0.107:6443 --token e901kz.cvfoa7b6d9 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:d8ccdaccc90507476cbeeea3f1943572e7cd4cd8e6638fa0
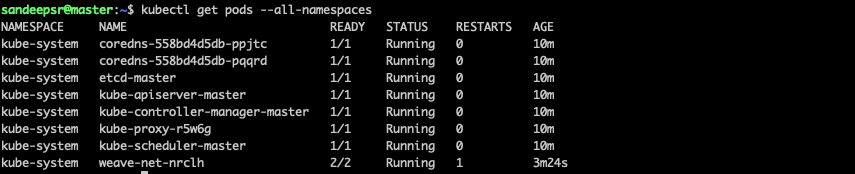
Install network add-on
For this demo we will use weavnet as our network add-on and I have copied the kubelet command from here
please run the below command in master vm only
kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"Join the nodes to cluster
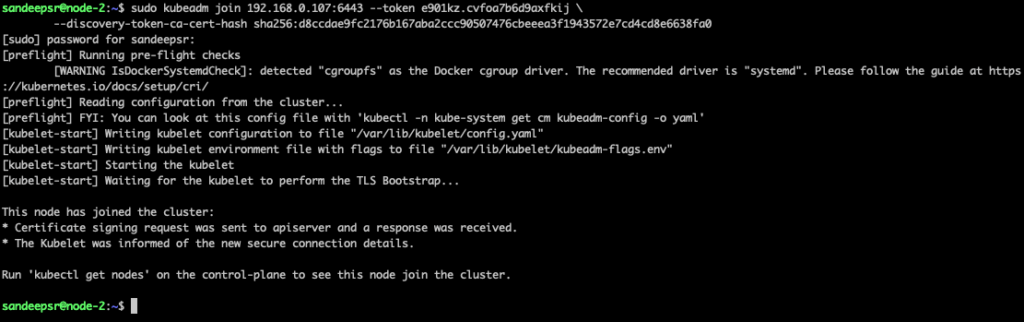
Since I already copied the join command from kubeadm init output , we can simply go execute it from nodes – in our case node-1 & node-2
Before join the nodes to cluster , lets see the nodes output
sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready control-plane,master 14m v1.21.1
Let’s join now by running the command in nodes
meanwhile I ran a watch command in master node and below is the output
sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl get nodes --watch NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready control-plane,master 17m v1.21.1 master Ready control-plane,master 18m v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 1s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 4s v1.21.1 node-1 NotReady 10s v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 31s v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 31s v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 34s v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 54s v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 61s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 0s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 3s v1.21.1 node-2 NotReady 10s v1.21.1 master Ready control-plane,master 23m v1.21.1 node-2 Ready 63s v1.21.1 node-2 Ready 63s v1.21.1 node-2 Ready 63s v1.21.1 node-2 Ready 65s v1.21.1
Let’s run the Kublet nodes command again and see the difference
sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready control-plane,master 26m v1.21.1 node-1 Ready 7m10s v1.21.1 node-2 Ready 3m14s v1.21.1
Create a POD
Let’s create few pods and see our lab setup working as expected
All the commands are running form master vm only
sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl run hello-world --image=hello-world pod/hello-world created sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl run httpd --image=httpd pod/httpd created sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl run nginx --image=nginx pod/nginx created
Here is the pod output
sandeepsr@master:~$ kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES hello-world 0/1 Completed 4 2m1s 10.36.0.1 node-2 httpd 1/1 Running 0 93s 10.44.0.1 node-1 nginx 1/1 Running 0 83s 10.36.0.2 node-2